General
Mumbai: BMC Keeps Aside Gargai Dam Project, Prefers Seawater Desalination

To address the annual water shortages and eliminate water cuts, the Brihanmumbai Municipal Corporation (BMC) has been exploring options for augmenting water resources. Two potential solutions emerged: desalination of seawater and the development of the Gargai water resources into a dam, supplying water to the Modak Sagar Lake.
Preventing Tree Cutting for Gargai Dam
The BMC’s study indicated that the construction of the Gargai dam would require the felling of approximately 2.5 lakh trees. With a focus on preserving the environment, the BMC has decided to prioritise the establishment of seawater desalination plants instead. The tendering process for the desalination project is expected to commence within the next two to three months.
“The study of BMC shows that around 2.5 lakh trees need to be cut to construct Gargai dam and we want to save those trees. Therefore, We have given first preference to the desalination of seawater plants. Tenders for the desalination project will be floated in the next two to three months
“On the other hand, a company has been selected for the construction of Gargai dam and a tender document is also being prepared. Thereafter, the permission of the state government will be taken and then work will begin. The estimated time of construction of Gargai dam is three years,” Additional Municipal Commissioner, (Project) P Velrasu said.
Progress on Gargai Dam Construction
Concurrently, the BMC has selected a company for the construction of the Gargai dam, and preparations for the tender document are underway. Once the state government grants permission, construction work on the Gargai dam is scheduled to begin. The estimated timeframe for completing the dam is three years.
Current Water Resources and Supply
To cater to the water needs of Mumbai, the city relies on seven dams: Upper Vaitarna, Modak Sagar, Tansa, Madhya Vaitarna, Bhatsa, Vihar, and Tulsi. These lakes collectively hold 14 lakh 47 million litres of water. The BMC supplies 3850 million litres of potable water daily, while the actual demand stands at 4200 million litres per day. The Hydraulic department of the BMC regularly assesses water stocks and formulates water management plans for the year.
Annual Water Cuts and Reserve Water Usage
During May and June, the BMC traditionally seeks permission from the state government to utilize reserve water stock from the Bhatsa and Upper Vaitarna lakes. Last year, all lake levels dipped by 11%, prompting the BMC to implement a 10% water cut in Mumbai. However, heavy rainfall in July led to the withdrawal of water cuts after 12 days. This year, the city is once again at risk of facing water cuts.
Maharashtra
Mumbai: Rickshaw driver beaten up in Vikhroli on suspicion of child theft, burqa-clad driver did this to collect fare, police claim
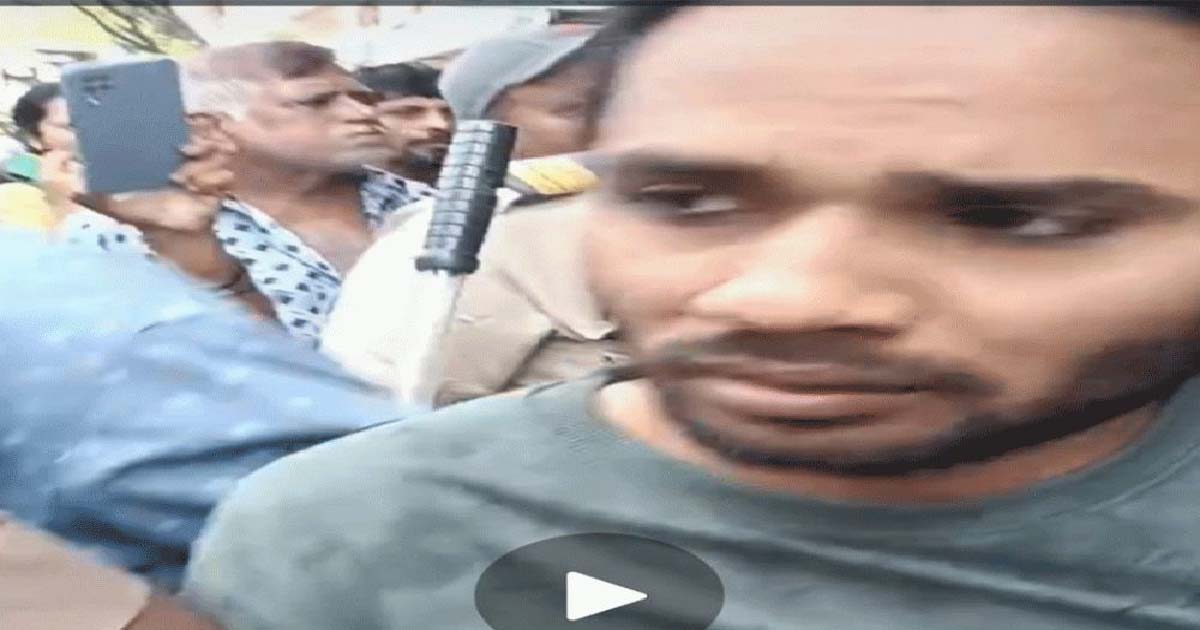
Mumbai: Vikhroli Park Site, after the rumor of a child theft, chaos broke out and an auto rickshaw driver was attacked by a mob when he went to the street of Vikhroli Madina Masjid dressed in a burqa to collect his fare. During this, people suspected that the child had come to steal, after which the mob beat him up, but the police reached the spot and then took him into their custody. During interrogation, it was found that the child had not come wearing a burqa to steal but to collect the fare. He was dressed in a burqa so that no one would recognize him and he could easily collect his fare and go back, but unfortunately, the people caught him and the police took him out of the mob’s possession and safely took him to the police station. After that, the police confirmed that the child had not come to steal. Further investigation is underway in this matter. The police said that along with the investigation, it is also being found out whether he really came to collect the fare or not. He is a thief. Initial investigation has revealed that the child is not a thief. The police have confirmed that the rickshaw driver is not a thief.
Maharashtra
Municipal Corporation in Mumbai is committed to conducting administration and election process in a fearless, free and transparent environment: Bhushan Gagrani
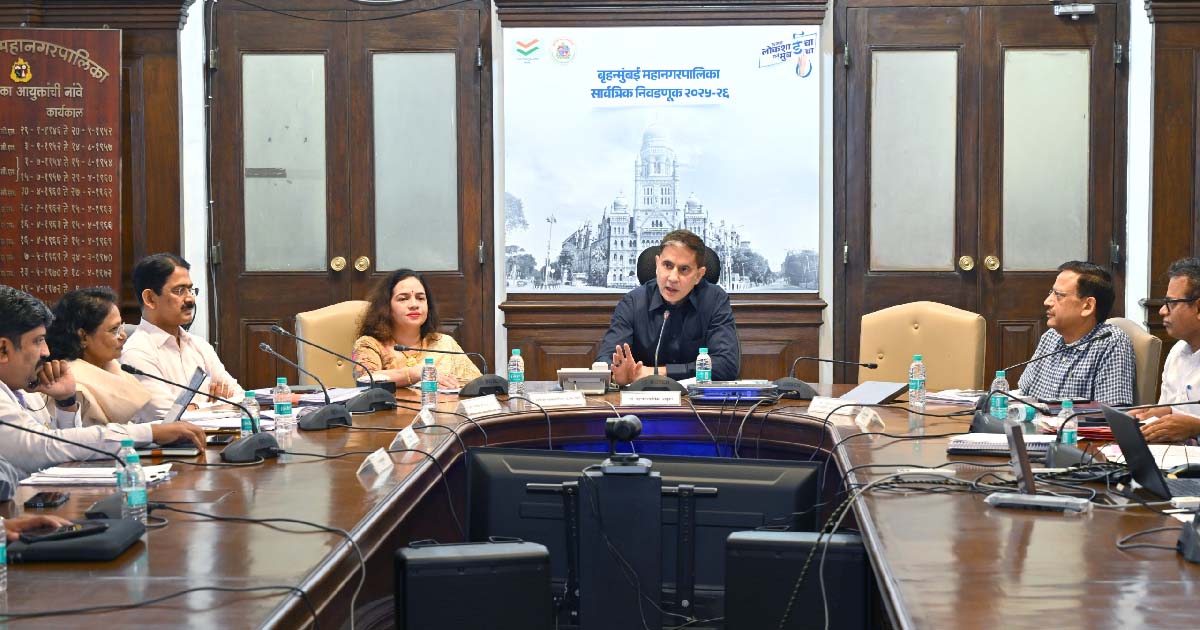

Mumbai: Municipal Corporation Administration and Election System Mumbai Municipal Corporation is committed to conducting the election process for the general elections 2025-26 in a completely fearless, free, transparent and disciplined environment. In this regard, the Mumbai Municipal Corporation Administration has made all and extensive preparations and all necessary measures are being implemented effectively. The role of political parties is very important in the election process. In order to promote democratic values and make the election process fair, transparent and credible, all political parties, their office bearers and workers should strictly follow the code of conduct framed by the State Election Commission and cooperate with the Municipal Corporation Administration. A positive and exemplary example should be set in the electoral process, this appeal was made by Municipal Commissioner and District Election Officer Bhushan Gagrani. A meeting was held with representatives of political parties at the Municipal Corporation headquarters today in connection with the Mumbai Municipal Corporation general elections 2025-26. On this occasion, Gagrani presented detailed information about various administrative, technical and legal aspects of the elections.
Additional Municipal Commissioner (City) Dr. Ashwini Joshi, Special Duty Officer (Election) Vijay Balmwar, Joint Commissioner (Tax Assessment and Collection) Vishwas Shankarwar, Assistant Commissioner (Taxation and Collection) Gajanan Belle, UP Election Officer Vijay Kumar Suryavanshi and other office bearers and representatives of various political parties were present in the meeting. Political parties were provided detailed information about the offices of 23 Election Decision Officers and their scope of work for the smooth conduct of the elections. Along with this, guidance was also given on the process of filing nomination papers, scrutiny of applications, registration of objections and how to contact these offices for day-to-day work in the election process. Municipal Commissioner Shri said that all necessary arrangements have been completed at the level of the Election Decision Officer so that the candidates do not face any technical problems.
Additional Municipal Commissioner (City) Dr. Ashwani Joshi said that all guidelines have been given so that the candidates do not make any mistakes while filing nomination papers (candidate applications) for the elections. The concerned persons should submit all the information in the prescribed format. Candidates should take special care that no application is rejected due to technical difficulties. It is mandatory for the candidates to fill all the information correctly and clearly in the affidavit submitted with their application. He said that if any column is left blank in the affidavit or if incorrect information is found, the nomination of the candidate, along with all other matters, can be cancelled.
Joint Commissioner (Tax Assessment and Collection) Vishwas Shankarwar said that the main objective of the administration is to increase the voting percentage to strengthen democracy. For this, political parties should create awareness among the voters. Public awareness is being created among the voters under the ‘SVEEP’ program by the Municipal Corporation. Also, it is mandatory to follow the guidelines of the esteemed State Election Commission regarding election expenses. Candidates should keep a record of every expense incurred during the election campaign and submit the account of election expenses within the stipulated time. Various doubts raised by the representatives of political parties on various issues were cleared including caste verification certificate, toilet usage certificate, Appendix 1 and Appendix 2, appointment of representatives of election candidates.
Maharashtra
Abu Asim Azmi praised for introducing a bill against hate speeches and hate crimes, Muslim organizations called Abu Asim Azmi’s step commendable.
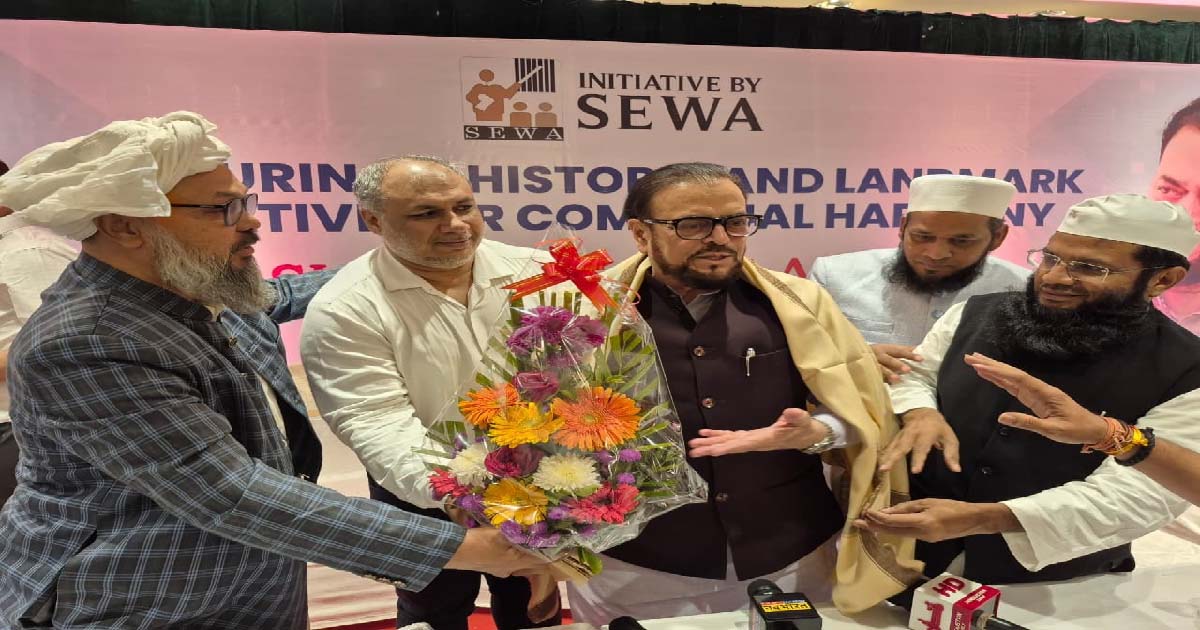

Mumbai: Leading Mumbai NGOs like OZ Seva Trust, Minara Masjid Trust, All India Ulema Board, Malik Liaquat Hussain Trust, National Uni-Ayush Activist Trust, Mumbai Central Association etc. today felicitated SP State President Abu Asim Azmi at Islam Gymkhana and appreciated his efforts to maintain unity and brotherhood in the society by respecting all religions in the Maharashtra Assembly. Azmi had introduced a bill in the Nagpur Assembly to enforce strict laws against religious hatred, blasphemy, prophets, religious leaders, and religious places, and hate speeches and hate crimes.
The event was organised at Islam Gymkhana, Mumbai. Addressing the event, Abu Asim Azmi said that nowadays hatred is being spread among the brothers by making objectionable or insulting inflammatory speeches against any religion, religious leader, religious book, religious place, Prophet Muhammad (PBUH). This poses a threat to peace and order. Therefore, we have presented this bill in the Legislative Assembly against those who insult any religion, religious leader, religious book, religious place, or Prophet. This bill proposes a penalty of imprisonment for up to 10 years and a fine of up to Rs 2 lakh for those who make slanderous statements about any religion, religious leader, religious book, or religious place or spread it on social media. Such a punishment will curb hate speech and hate crimes. MLA Raees Shaikh, State Working President Yousuf Abrani, Chief General Secretary Meeraj Siddiqui and Advocate Rizwan Merchant, Maulana Ijaz Kashmiri, Nizamuddin Rain, Naseem Siddiqui, Sarfaraz Arjo were present at the event.
-

 Crime3 years ago
Crime3 years agoClass 10 student jumps to death in Jaipur
-

 Maharashtra1 year ago
Maharashtra1 year agoMumbai Local Train Update: Central Railway’s New Timetable Comes Into Effect; Check Full List Of Revised Timings & Stations
-

 Maharashtra1 year ago
Maharashtra1 year agoMumbai To Go Toll-Free Tonight! Maharashtra Govt Announces Complete Toll Waiver For Light Motor Vehicles At All 5 Entry Points Of City
-

 Maharashtra1 year ago
Maharashtra1 year agoFalse photo of Imtiaz Jaleel’s rally, exposing the fooling conspiracy
-

 National News1 year ago
National News1 year agoMinistry of Railways rolls out Special Drive 4.0 with focus on digitisation, cleanliness, inclusiveness and grievance redressal
-

 Maharashtra1 year ago
Maharashtra1 year agoMaharashtra Elections 2024: Mumbai Metro & BEST Services Extended Till Midnight On Voting Day
-

 National News1 year ago
National News1 year agoJ&K: 4 Jawans Killed, 28 Injured After Bus Carrying BSF Personnel For Poll Duty Falls Into Gorge In Budgam; Terrifying Visuals Surface
-

 Crime1 year ago
Crime1 year agoBaba Siddique Murder: Mumbai Police Unable To Get Lawrence Bishnoi Custody Due To Home Ministry Order, Says Report












